How do bees pollinate?
 Aug 25,2022
Aug 25,2022
 Lucia Ma
Lucia Ma
How do bees pollinate? With the development of agriculture, large-scale planting and greenhouse planting crops have become common planting patterns. The disadvantage of these two planting patterns is that they are prone to lack of natural insect pollination. In order to increase the fruit set rate of crops, growers generally choose to hire people to conduct artificial pollination. So how do bees pollinate? What is the difference between bee pollination and artificial pollination? Let's find out!
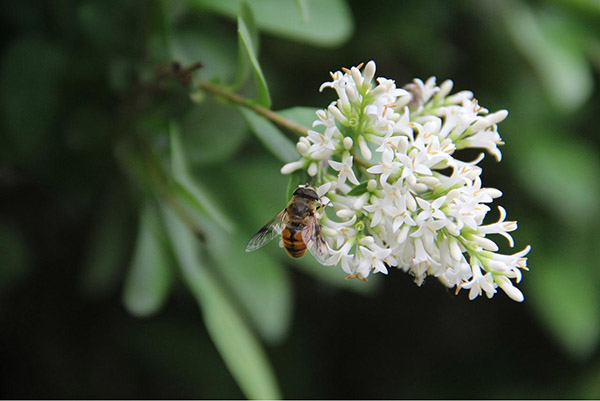

How bees pollinate
Spring fruit bees pollinate, not its original intention. Because bees collect pollen for their own bee food and nectar to make honey. When collecting pollen and nectar (the pollen is collected in the "pollen baskets" of its legs), some of the pollen will stick to its head, body, and legs, and when it reaches another flower, it is likely to collect it. The pollen sticks to its stigma, thus completing the whole process of pollination.

What is the difference between bee pollination and artificial pollination
1. Advantages (1) The pericarp of bees is densely populated with downy hairs, which are bifurcated, which is conducive to the adhesion of pollen, and the hind feet are specialized into pollen baskets that can store and carry pollen. It is calculated that the pollen carried by a bee can reach 500 Even if the pollen mass is removed, there are still 10,000 to 25,000 seeds, and bees are social animals with a large number of individuals, so the pollination efficiency is higher than that of artificial pollination. (2) The fruit setting rate of bee pollination is higher than that of artificial pollination. (3) Manual pollination requires a lot of labor, and it is easy to damage the stamens during the artificial pollination process, and it cannot ensure that the pollen is evenly spread.
2. Disadvantages (1) The pollination effect of bees is not ideal for certain crops, such as tomatoes. (2) Bees have poor moisture tolerance and strong phototaxis, so they are not suitable for pollination of greenhouse vegetables. (3) In winter, bee colonies generally do not go out to collect honey, so in winter, bees cannot be used for pollination.




 Tel:
Tel:

 Home
Home How to get rid of ants in beehives?
How to get rid of ants in beehives?  You May Also Like
You May Also Like







 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address







